Rapid fFN®
Improving women’s health is at the core of Hologic’s technology and products. One essential pillar in the Hologic Diagnostic Solutions portfolio is perinatal testing. The Rapid fFN® test is a safe, reliable, and non-invasive test that can help providers determine a pregnant woman’s risk of delivering preterm.

Overview
Documents
Training
Don't wonder
if sending her home is the right decision...
Be confident
that it is.
The use of fetal fibronectin (fFN) testing can help reduce unnecessary admissions and hospitalizations and help direct care and resources to patients who need it most.
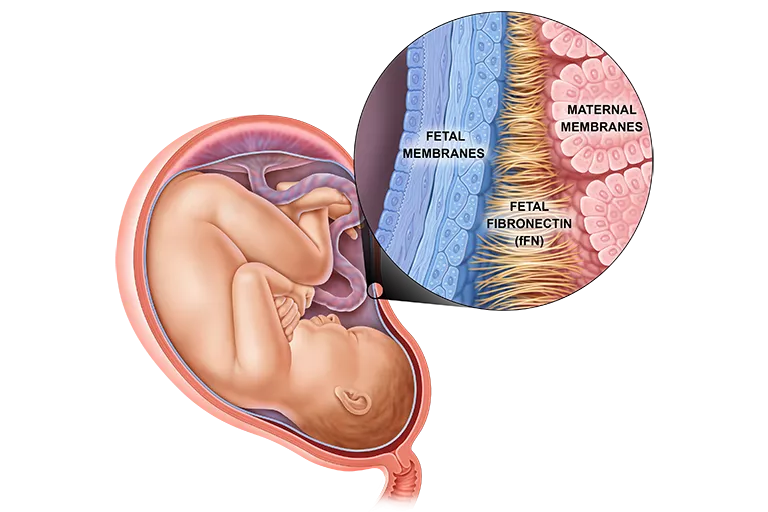
Fetal Fibronectin: A powerful predictor of preterm birth
fFN is an adhesive glycoprotein found at the maternal-fetal interface which functions like a glue to bind the baby to the uterus during fetal development.1 fFN is generally absent in vaginal secretions during weeks 16 to 35 of gestation, so if fetal fibronectin is detectable in vaginal discharge during pregnancy weeks 22-35, it means that the protein is “leaking.” This can alert healthcare providers that the patient is at risk of preterm birth.
The Healthcare Benefits of fFN Testing
-
Timely and appropriate interventions, such as antenatal steroids and magnesium sulfate.
- Avoidance of unnecessary hospitalizations. One study showed that the average length of stay for patients with symptoms of preterm labor was reduced from 5.2 days to just 0.6 days after fFN testing was adopted.3
- Effective transfer of patients at high risk of imminent preterm birth to a hospital with an appropriate NICU.

Interpreting Results
Negative Result2
-
Approximately 80% of patients will get a negative result.
-
A negative result means that patients have a less than 1% chance of giving birth in the next two weeks.
-
A negative result can help avoid unnecessary drug treatments, bed rest and hospitalizations. This knowledge can also provide peace of mind, freeing patients to continue with current activities without unnecessarily cancelling or rescheduling plans.
-
The Rapid fFN test can be repeated as often as every 2 weeks to monitor ongoing risk.
Positive Result2
-
Approximately 20% of patients will get a positive result
- A positive result means the body is "leaking" fetal fibronectin, a sign that the patient may be preparing to give birth.
- A positive result does not necessarily mean the patient will deliver soon, but it will alert the doctor to the fact that they are at higher risk for preterm labor.
- The Rapid fFN test can be repeated as often as every 2 weeks to monitor ongoing risk.
Ordering Information
1. Rapid fFN for the TLiIQ System [package insert]. AW-24196-001, Rev. 001. 2. Centers for Disease Control. Preterm Birth. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/maternalinfanthealth/pretermbirth.htm. Updated June 26, 2017. Accessed May 21, 2020. 3. Abenhaim HA, et al. Does availability of fetal fibronectin testing in the management of threatened preterm labour affect the utilization of hospital resources? J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2005;27(7):689-94. doi:10.1016/S1701-2163(16)30547-3.
Safety Data Sheets
Package Inserts
Related Products
Rapid fFN®
Improving women’s health is at the core of Hologic’s technology and products. One essential pillar in the Hologic Diagnostic Solutions portfolio is perinatal testing. The Rapid fFN® test is a safe, reliable, and non-invasive test that can help providers determine a pregnant woman’s risk of delivering preterm.

Overview
Package Inserts
Preterm birth is a serious problem
Preterm birth is defined as delivery before 37 weeks gestation. Globally, an estimated 15 million babies are born prematurely. Preterm birth complications are the leading cause of death among children under five years of age, resulting in nearly one million deaths each year.1
Babies born prematurely may have more health problems at birth than babies born at term.2 While some problems related to preterm birth can be treated, others can cause long-term developmental problems or learning disabilities.3 With proper knowledge of preterm birth risk and appropriate healthcare professional planning, many of these threats can be better managed.
Quantitative data for a more complete answer:
the PeriLynxTM System
When it comes to preterm birth, establishing the risk of delivery is key. Hologic’s quantitative Rapid fFN Test on the PeriLynx System gives healthcare professionals valuable information in a matter of minutes. This information can be used with other clinical information to help manage care and determine treatment choices for patients who are either experiencing symptoms of preterm delivery or for asymptomatic patients who meet the high risk criteria, such as women who have had a previous preterm delivery or women who are carrying twins or triplets.
Obtaining quantitative fetal fibronectin (fFN) data ultimately helps healthcare professionals stratify a patient’s individual risk for preterm birth, which assists with the development of a suitable management plan. Using this and other diagnostic data, allows healthcare professionals to make better-informed decisions about which patients should be admitted for treatment, observed for further diagnosis, transferred to a specialist hospital or discharged.
More information and less guesswork with quantitative fFN testing
The quantitative Rapid fFN test precisely measures the fFN concentration in cervicovaginal secretions, providing healthcare professionals with an indication of the risk of preterm birth based on the fFN measurement in ng/mL.
Fetal fibronectin (fFN) is a "glue-like" protein that binds the membranes around the baby to the uterus. It is detectable in vaginal secretions at the very beginning of pregnancy, when this bond is first forming, and then again at the end of pregnancy.4 fFN is generally absent in vaginal secretions during weeks 16 to 35 of gestation, so if it is detected during this time, it means that the protein is “leaking”. This can alert healthcare professionals that the patient is at risk of preterm birth.4
The quantitative Rapid fFN test allows healthcare professionals to give women who are at low risk of preterm birth peace of mind in knowing that they are unlikely to deliver in the next 7 or 14 days. For women whose fFN results indicate a high risk of preterm birth, healthcare professionals can intervene early to provide optimal patient care.
The quantitative Rapid fFN test is approved for collection between 22-36 weeks with symptomatic patients and 18-28 weeks with asymptomatic high-risk patients.
The Healthcare Benefits of Quantitative fFN Testing
The quantitative Rapid fFN test is one of several tools available to help healthcare professionals determine the best course of action for patients with symptoms of preterm labor. Benefits of fFN testing include increased efficiencies, without compromising clinical outcomes. These benefits are achieved through:
- Timely and appropriate interventions, such as antenatal steroids and magnesium sulphate, and likewise avoidance of unnecessary interventions or transfers for those at lower risk.
- Avoidance of unnecessary hospitalizations. One study showed that the average length of stay for patients with symptoms of preterm labor was reduced from 5.2 days to just 0.6 days after fFN testing was adopted.5
- Effective transfer of patients at high risk of imminent preterm birth to a hospital with an appropriate NICU.



