Aptima® Mycoplasma genitalium Assay
A highly sensitive NAAT that seamlessly integrates into your lab's workflow to confirm M. gen.

Overview
Documents
Training
A highly prevalent STI you can now accurately identify.
Mycoplasma genitalium (M. gen) is an often misdiagnosed sexually transmitted infection (STI) with similar clinical presentation to chlamydia, gonorrhea and trichomoniasis.1,2 Testing for M. gen is recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for patients with persistent or recurrent cervicitis and urethritis, and should be considered for those with pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).3
Avoid Outdated Methods
Conventional testing methods such as microscope and culture have made M. gen difficult to identify.3
Prioritize Accuracy
A highly sensitive rRNA test is needed for accurate diagnosis, as it provides a more abundant target than DNA.4
Choose the Right Test
Each M. gen organism contains 1000s of rRNA copies versus only one copy of DNA, making an RNA-based nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) more sensitive than a DNA-based test.4
Receiving the Right Diagnosis
The Aptima Mycoplasma genitalium assay offers a sensitive, rRNA-based NAAT that can detect characteristically low M. gen bacterial loads.5,6
- CDC recommends NAAT to detect M. gen infection3
- First FDA-cleared assay for M. gen7
- rRNA-based Aptima Mycoplasma genitalium assay provides up to 100% sensitivity. DNA-based tests can miss up to 40% of infections8
Often Overlooked
When there are symptoms, M. gen can present similarly to other urogenital tract bacterial infections. Overlapping symptoms can include abnormal discharge, vaginal irritation and pain during urination or sex.1,2
Adverse Health Outcomes
When left untreated, M. gen infections can result in serious health consequences.9
Highly Prevalent
Among women, M. gen prevalence is 10.2% and detected in 10-30% of clinical cervicitis cases and up to 22% of PID cases. Among men, M. gen prevalence is 10.6% and detected in 40% of recurrent urethritis cases.3,10
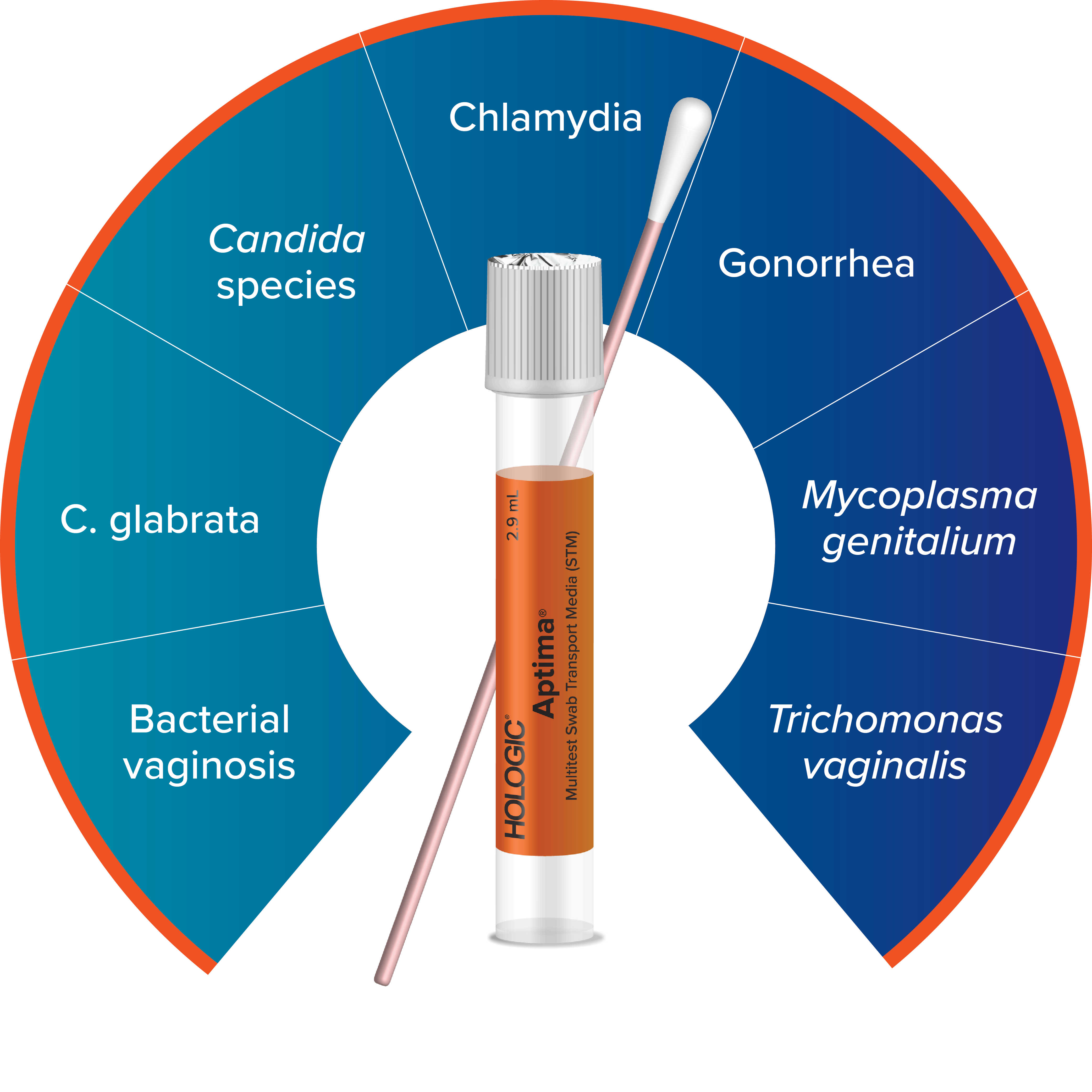
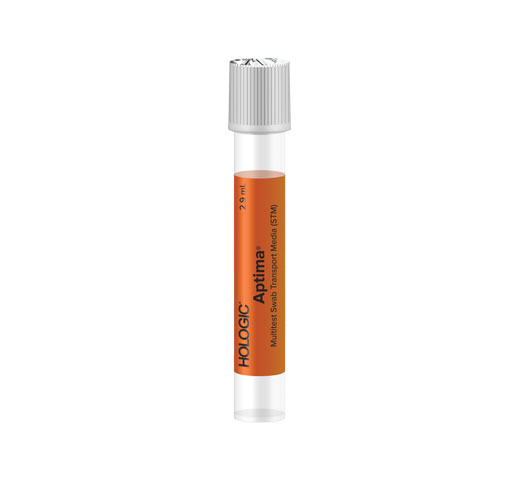
Expand Your Offering with the Aptima® Multitest Swab
Testing for M. gen can be done using the Aptima Multitest Swab. The complete Aptima STI portfolio powers efficient, streamlined testing with assay and collection consolidation for sexual and vaginal health.
Aptima® Sexual and Vaginal Health Solution
Learn how our tests help patients protect their sexual and reproductive health.

Latest News on Aptima Sexual and Vaginal Health
Evidence. Insight. Engagement.
Explore resources on Hologic’s Medical Education site to learn more about our innovative technology, view the latest clinical and scientific evidence and see how you can help improve patient care.