Aptima® CMV Quant Assay
FDA-Approved solution to reliably and efficiently deliver actionable viral load insights to post-transplant patients and their care teams.
Overview
Documents
Training
CMV and Viral Load Monitoring
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is a common complication that affects organ transplant patients. CMV, a member of the herpes virus family, establishes a lifelong latent infection that is generally asymptomatic. However, in immunocompromised patients, such as transplant recipients, reactivation of latent CMV is often life-threatening. Guidelines recommend regular monitoring of CMV viral load as an aid for diagnosis of CMV infections and monitoring response to treatment.1, 2
The Aptima CMV Quant assay intended use is to:
Monitor Viral Load
Assess viral response to treatment with
serial DNA measurements in patients receiving
anti-CMV therapy.
Inform Care
Aid in the management of solid-organ transplant patients and hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients.
The Latest on Aptima Virology

“We have a legacy of innovation in viral load testing, and our Aptima CMV Quant assay is the first in a series of quantitative assays to support patient care following transplant surgery. We’re committed to providing our laboratory partners with superior solutions that improve workflow efficiency and address the challenges faced by today’s molecular lab.”
CMV by the Numbers
A member of the herpes family, CMV causes fever, pain, sore throat, fatigue and weight loss. It can threaten the hope of a healthy future for patients with an organ or stem cell transplant.
12
Number of weeks after transplant surgery that most patients are monitored weekly for CMV2.

1/2
of all adults have been infected with CMV by age 403.

20-60%
of transplant recipients develop a symptomatic CMV infection4.
32%
of organ transplant recipients experience a recurrent CMV infection after prolonged antiviral use5.
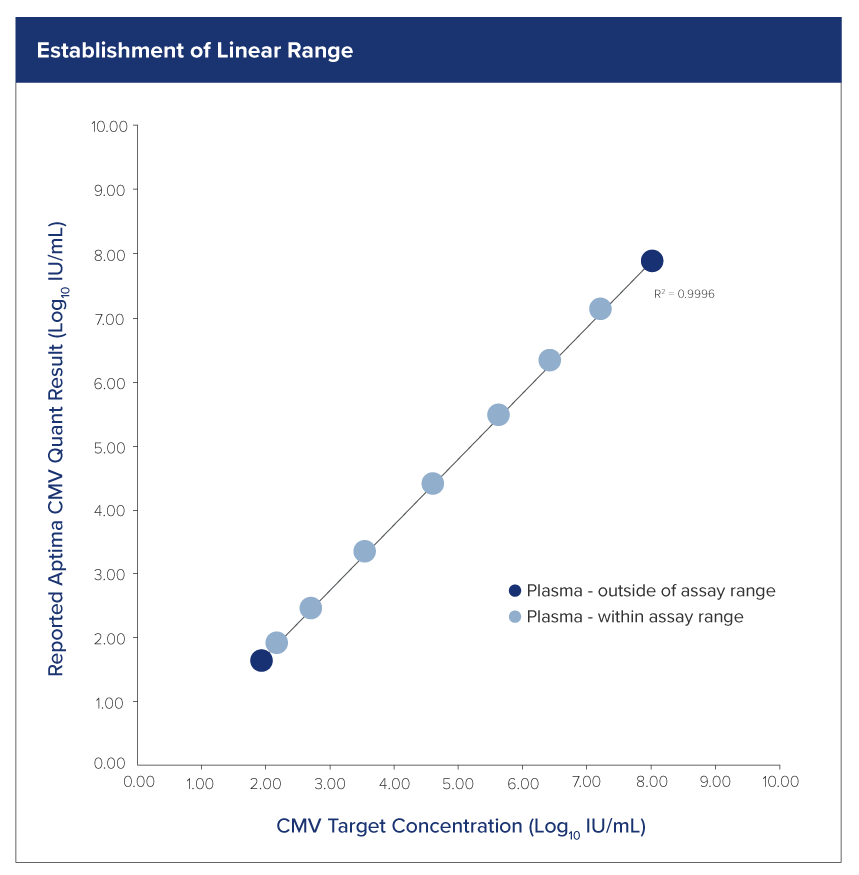
Excellent performance for high-quality results
Deliver accurate, consistent, and clinically actionable viral load insights with our extensively-validated quantitative CMV assay.
Sensitivity:
- LoD – 40.7 IU/mL plasma
- LLoQ – 53 IU/mL plasma
Specificity:
- 99.7% plasma
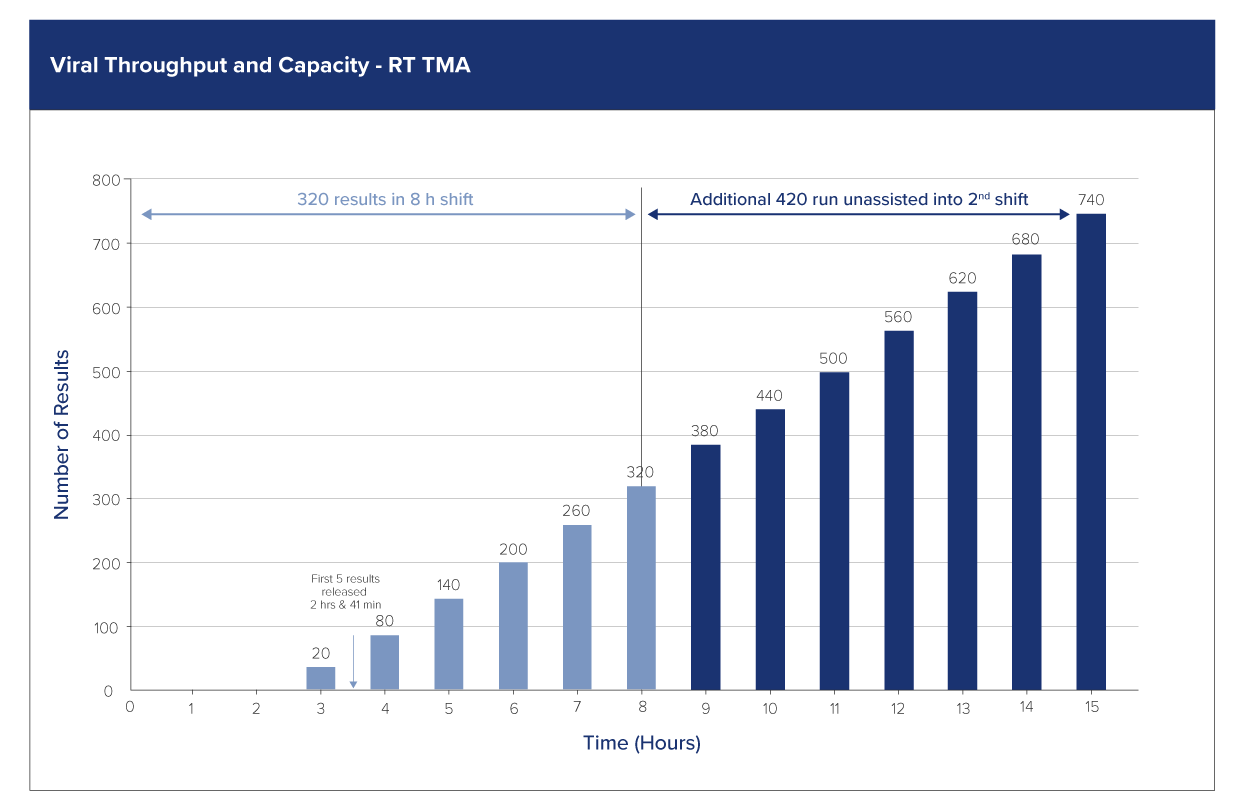
Efficient workflow for a productive lab
Improved laboratory workflow with the Aptima CMV Quant Assay on the Panther® system.
Fully automated with random access and LIS integration
- Reduce hands-on time
- Time-to-result in ~2h 40 min
1-touch tube standardization
- Direct loading of plasma primary tube (500 uL)
- No manual sample extraction required for less operator error
- No individual tubes transfers between platforms or between labs
Run Aptima CMV Quant assay in parallel with our core viral assays: Aptima® HIV-1 Quant Dx, Aptima® HCV Quant Dx, and Aptima® HBV Quant assays
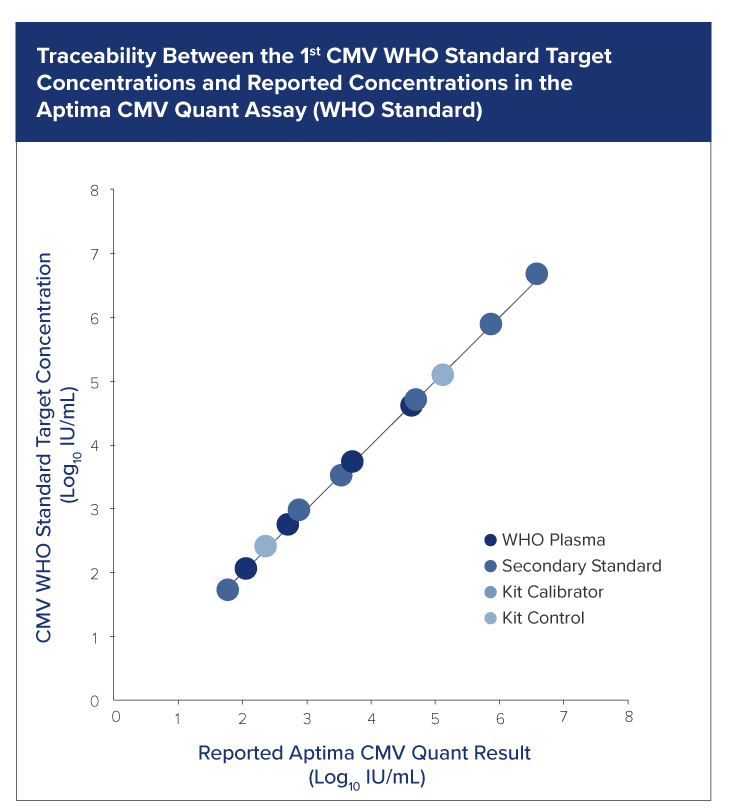
The highest degree of standardization
Ensure multisite accurate performance to reliably monitor transplant patients’ viral load trends over time and across geographies with the Aptima CMV Quant assay.
Guideline driven
- Completely aligns with the 1st WHO International Standard.
Consistent Reproducibility
- Uses the same panel of samples to evaluate across multiple operators, instruments and locations to deliver consistent results across all variables.
Claim
Quant
LoD
40.7 IU/mL plasma
LLoQ
53 IU/mL plasma
Methodology
RT-TMA
Verified Sample Type
Plasma (EDTA, PPT)
One reliable partner
Trust in a single lab partner to maximize your lab’s operational efficiencies.
Expanding menu
With 19 FDA-approved assays and an ever growing menu with 7 assays in development, you can now integrate and consolidate transplant and core viral load assays on a single high-throughput system.
Consolidation efficiencies
Help reduce LIS connection costs, streamline tech training, and drive cost efficiencies in lab purchasing and resource management with consolidation of platforms.
Excellent customer service
Our award-winning customer service means you are one call away from a large team that supports all your reagent needs.
1. Kotton, Camille N; Kumar, Deepali; Caliendo, Angela M; Huprikar, Shirish; Chou, Sunwen; Danziger-Isakov, Lara; Humar, Atul (2018). The Third International Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Cytomegalovirus in Solid-organ Transplantation. Transplantation, 102(6):900-931. 2. Razonable AA, Humar A. Cytomegalovirus in solid organ transplant recipients-Guidelines of the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin Transplant. (2019) 33(9). 3. CDC. About Cytomegalovirus (CMV). Cytomegalovirus and congenital CMV Infection. Last Reviewed August 18, 2020. Accessed March 7, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/cmv/overview.html 4. Hibberd PL, et al. Symptomatic cytomegalovirus disease in the cytomegalovirus antibody seropositive renal transplant recipient treated with OKT3. Transplantation. 1992 Jan;53(1):68-72. 5. Natori Y, et al. Recurrence of CMV Infection and the Effect of Prolonged Antivirals in Organ Transplant Recipients. Transplantation. 2017 Jun;101(6):1449-1454.
Disclaimers:
* The Aptima SARS-CoV-2, Aptima Zika Virus, Aptima SARS-CoV-2/Flu and Panther Fusion SARS-CoV-2 assays have not been FDA cleared or approved: These tests have been authorized by FDA under an EUA for use by authorized laboratories; The Aptima and Panther Fusion SARS-CoV-2 assays have been authorized only for the detection of nucleic acid from SARS-CoV-2, not for any other viruses or pathogens; The Aptima Zika Virus assay has been authorized only for the detection of nucleic acid from Zika virus, not for any other viruses or pathogens; The Aptima SARS-CoV-2/Flu assay has been authorized only for the simultaneous qualitative detection and differentiation of nucleic acid from SARS-CoV-2, influenza A virus, influenza B virus, and not for any other viruses or pathogens. The Aptima SARS-CoV-2, Panther Fusion SARS-CoV-2, and Aptima SARS-CoV-2/Flu assays are only authorized for the duration of the declaration that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of emergency use of in vitro diagnostic tests for detection and/or diagnosis of COVID-19 under Section 564(b)(1) of the Act, 21 U.S.C. § 360bbb-3(b)(1), unless the authorization is terminated or revoked sooner. The Aptima Zika assay is only authorized for the duration of the declaration that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of emergency use of in vitro diagnostic tests for detection of Zika virus and/or diagnosis of Zika virus infection under Section 564(b)(1) of the Act, 21 U.S.C. § 360bbb-3(b)(1), unless the authorization is terminated or revoked sooner.
† In development and not for sale.
Safety Data Sheets
Package Inserts
Explore the data
Learn more about the Aptima® CMV assay on the Panther® system.
Related Products
Aptima® CMV Quant Assay
Accurate results for a successful patient monitoring and treatment strategy.

Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is member of Herpesviridae Family and is an enveloped, double-stranded DNA virus. Globally, 40-60% of the adult population have had prior CMV infection and could exceed 90% in some patient populations.1 CMV is usually asymptomatic in healthy individuals but remains in the body in a latent state. For patients undergoing solid organ or hematopoietic stem cell transplant, CMV infection and reactivation can lead to serious complications. If left untreated, CMV infection can lead to severe disease, transplant rejection, and death.
The Third International Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Cytomegalovirus recommends quantitative nucleic acid amplification testing (QNAT) as the preferred method of monitoring CMV infection in patients post transplantation.2 This use of QNAT assays calibrated to the World Health Organization (WHO) International Standard, like the Aptima CMV Quant assay, decreases variability in results resulting.